TR2026-006
RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer
-
- , "RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer", Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), December 2025.BibTeX TR2026-006 PDF Software
- @inproceedings{Kato2025dec,
- author = {Kato, Sorachi and Yataka, Ryoma and Wang, Pu and Miraldo, Pedro and Fujihashi, Takuya and Boufounos, Petros T.},
- title = {{RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer}},
- booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)},
- year = 2025,
- month = dec,
- url = {https://www.merl.com/publications/TR2026-006}
- }
- , "RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer", Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), December 2025.
-
MERL Contacts:
-
Research Areas:
Abstract:
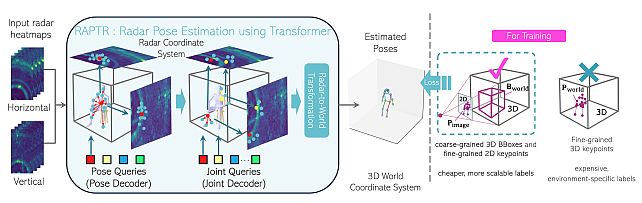
Radar-based indoor 3D human pose estimation typically relied on fine-grained 3D keypoint labels, which are costly to obtain especially in complex indoor set- tings involving clutter, occlusions, or multiple people. In this paper, we propose RAPTR (RAdar Pose esTimation using tRansformer) under weak supervi- sion, using only 3D BBox and 2D keypoint labels which are considerably eas- ier and more scalable to collect. Our RAPTR is characterized by a two-stage pose decoder architecture with a pseudo-3D deformable attention to enhance (pose/joint) queries with multi-view radar features: a pose decoder estimates initial 3D poses with a 3D template loss designed to utilize the 3D BBox labels and mitigate depth ambiguities; and a joint decoder refines the initial poses with 2D keypoint labels and a 3D gravity loss. Evaluated on two indoor radar datasets, RAPTR outperforms existing methods, reducing joint position error by 34.3% on HIBER and 76.9% on MMVR. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/merlresearch/radar-pose-transformer.
Software & Data Downloads
Related Publication
- @article{Kato2025nov,
- author = {Kato, Sorachi and Yataka, Ryoma and Wang, Pu and Miraldo, Pedro and Fujihashi, Takuya and Boufounos, Petros T.},
- title = {{RAPTR: Radar-based 3D Pose Estimation using Transformer}},
- journal = {arXiv},
- year = 2025,
- month = nov,
- url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.08387}
- }